
Sales Department Structure and Roles: How to Organize the Work of a Successful Sales Team
In this article, we will briefly explain the types of sales department organization models and the roles that can be found in sales teams. We cover all the basics of creating a great sales department structure.
What Is Sales Department Structure?
The term sales department structure refers to the division of the sales team and the definition of the goals and tasks of all members of the sales department. In simple terms, it is about dividing tasks within the sales department to improve the performance of the entire department.
The structure of the sales team depends, of course, on many factors, such as the size of the team, the regions served, the number of customers, the type of product, and the complexity of the sales process.
Below, we will outline the basic types of organizational structures of sales departments and explain what roles and positions can be found in sales departments today.
Why Is Having the Right Sales Structure So Important?
But before we go any further, let us consider why it is so important to introduce a proper organizational structure in a sales organization. After all, in the past, sales representatives performed all activities independently and there was no specific division of responsibilities.
However, a properly implemented sales team structure helps improve sales efficiency and ultimately enables business growth.
- It is easier for people to focus on their work when they know exactly what their responsibilities are and what sales goals they need to achieve.
- A proper sales model will boost your team’s performance.
- There are fewer conflicts when everyone knows what they should be doing.
Check also: 10 Phone Selling Negotiation Techniques That Will Boost Your Sales
Sales Department Structure—Different Roles
Below are some common, as well as some lesser-known, sales team job titles. Of course, for smaller companies, not all of these roles should have separate positions. The final division of responsibilities also depends on the product being sold.
However, it is worth considering who in our company performs the tasks associated with a given position and perhaps thinking about shifting some of the responsibilities from the salesperson’s shoulder.
Vice President of Sales
The vice president of sales is responsible for the overall management of the sales team. Their most important tasks include creating sales strategies and setting KPIs, organizing the work of the team, developing the team, recruiting and leading employees, and monitoring their performance.
Sales Managers (or Sales Leaders)
The sales manager is a lower position than the vice president of sales, but it has similar requirements. This position exists in smaller companies (where there is no vice president or chief revenue officer) or, conversely, in large organizations where the sales force is so numerous that the vice president needs help managing several sales teams.
Account Executives (or Account Managers)
An account executive is a senior member of the sales department. Their role is to work with high-potential clients and finalize the sales process.
Typically, an account executive works on selected leads with higher sales potential. Their job is to prepare an offer that meets the customer’s needs and will ultimately lead to closing the deal.
Sales Development Representatives
A sales development representative is a junior member of the sales team. They usually work in the first part of the sales process, and, at some point, they transfer the transaction to an account executive.
The responsibilities of this position depend on the company’s sales strategy. Typically, a sales development representative (SDR) is responsible for qualifying leads, taking care of low-quality inbound leads, or completing the first stage of outbound sales.
Customer Success Managers
Customer success representatives are responsible for maintaining good customer relationships. Their main role is communicating with the customer after the sales process is completed and introducing them to the product. Customer success managers (CSM) are also responsible for upselling and cross-selling products to existing customers and keep track of customer success metrics.
Sales Engineers
Sales engineers often play a role in companies offering high-tech or customized products. Their job is to support sales representatives in developing products or offers so that they meet customer expectations while remaining implementable. Sales engineers coordinate between the sales department and the technical team and must have a deep knowledge of products and technical limitations.
Sales Assistants
A large part of the sales team’s work is paperwork: for example, preparing proposals, NDAs, and contracts, sending invoices, conducting research, and updating databases.
These simple and repetitive tasks can take up a lot of time. For this reason, sales teams are often supported by sales assistants, who can perform some minor tasks for the sales team to help them focus on their top priorities.
Check also: Clients-Convert-Clients Marketing: Your Secret Sales Weapon
The Three Most Popular Types of Sales Team Structures
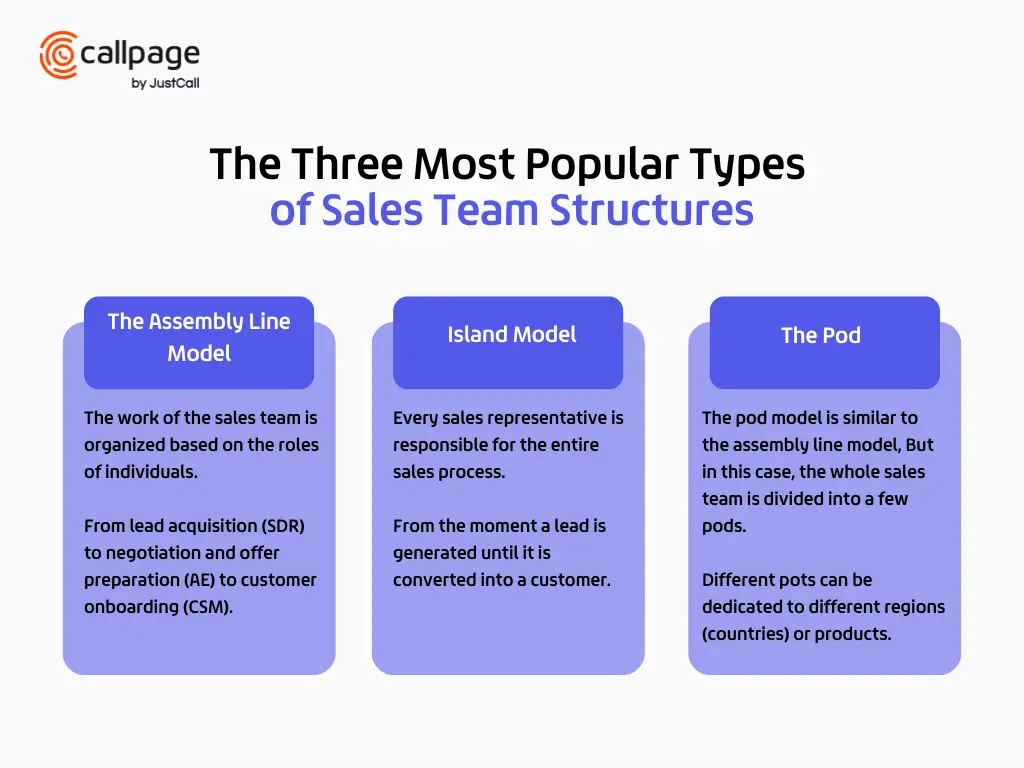
The Assembly Line Model
The name assembly line explains in large part the essence of this model. In the assembly line model, the work of the sales team is organized based on the roles of individuals. In this model, prospects are moved between team members—from lead acquisition (SDR) to negotiation and offer preparation (AE) to customer onboarding (CSM).
Here are a few advantages of the assembly line model:
- Different tasks require different skills; this sales team structure allows individuals to utilize their best skills.
- The team works together to achieve success; a new deal is the mutual success of every team member.
- Your best employees do not waste their time on unprofitable tasks or low-quality leads.
Island Model
In the island model, the sales representative is responsible for the entire sales process—from the moment a lead is generated until it is converted into a customer.
This organization of sales departments appears mainly in smaller companies or local businesses. It is also often used in companies with a very simple sales process with very little contact. From the sales team leader’s point of view, the organization of the work in this structure is very easy. All sales reps have the same goal—a sale.
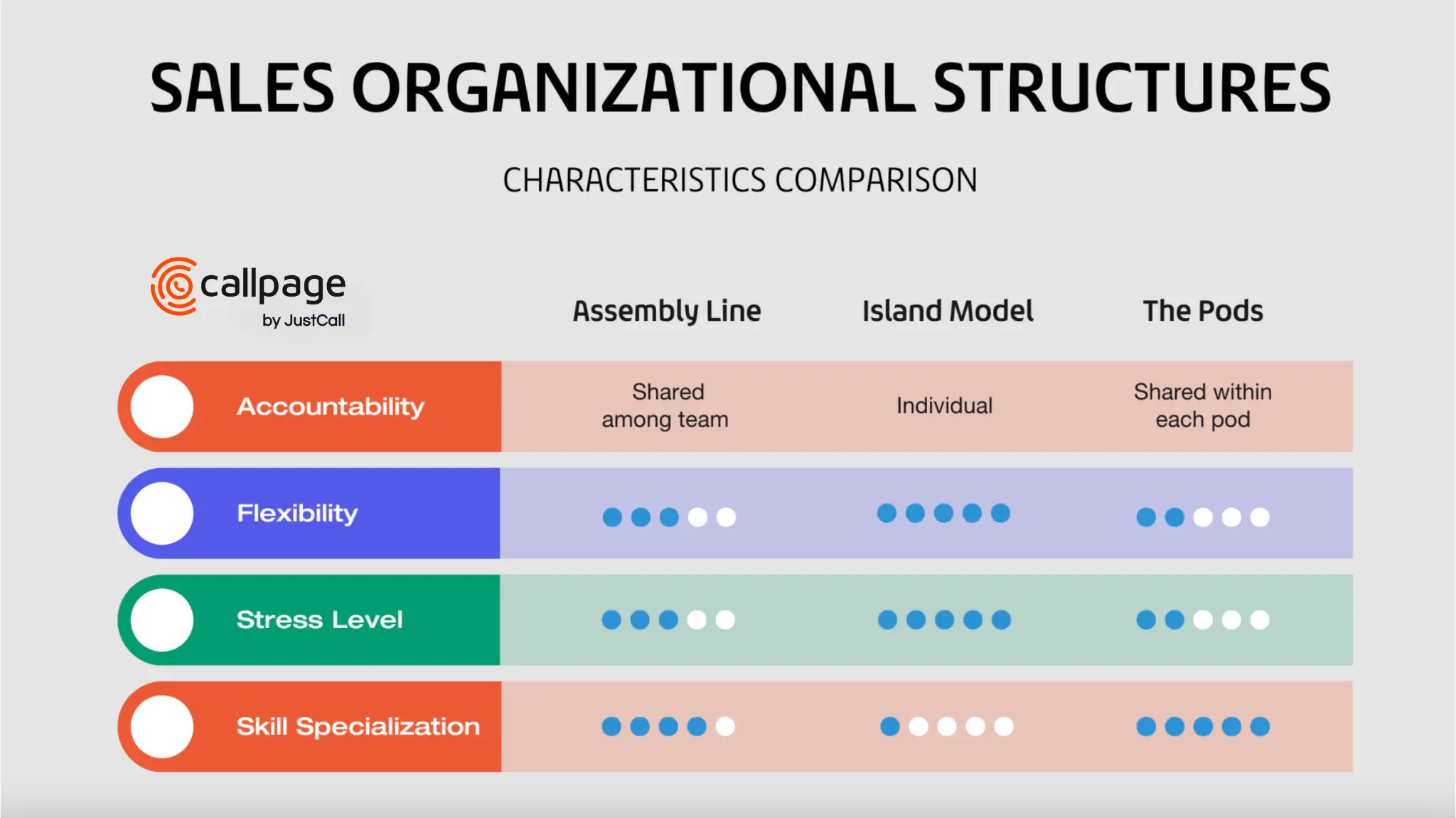
Certainly, the advantage of this sales organizational structure is competition between representatives and clear accountability for the success or failure of the process. However, it also has certain disadvantages—a high stress level, faster burnout of employees, a lack of focus on specific duties, and a lack of opportunity to benefit from individual employees' predispositions.
The Pod
The pod model is similar to the assembly line model, but it is usually used by large organizations. The main resemblance is the separation of the various stages of the process between different roles in sales teams, from SDR to CSM.
But in this case, the whole sales team is divided into a few pods. Different pots can be dedicated to different regions (countries) or products. Each pod has specialized representatives who handle prospects in different stages of a sales cycle.
Takeaways
Creating the right sales organization structure is key to the proper functioning and management of the sales team. However, sales leaders should not base their choices solely on the resources and size of the company. Even a small team can implement an assembly line sales model. The key is to select the model that will work best in your market and for your product.
Check also: How a Great Marketing Team Structure & Culture Improve Overall Effectiveness
Check out other posts
Start generating leads today!
Start a 14-day free trial now,
set up the widget on your site, and see how many more leads you can capture with CallPage
- No credit card required
- 10 minutes set up
- 14 days fully-features free trial